Form Checkbox (many to many)
This page will help you how to create and use a many to many relationships.
Table of contents
- What is many to many relationship?
- Creating Model (mood and post category ship)
- Checkbox to select multiple moods
- What is n+1 query problem?
- Select2
What is many to many relationship?
The many to many is a common relationship in our database. If your two models have has_many associations, you can say they are many to many relationships.
You can check Active Record Associations for more details.
Creating Model (mood and post category ship)
First, we need two Active Record models, let’s say post and mood.
So the relationship will be, post can belong to many moods and a mood can have many posts. So an associate model is required. We will name it PostMoodShip.
We have already the post model, so we need to create the mood and post_mood_ship models. Open your project container then run the rails g model mood.
root@0122:/usr/src/app# rails g model mood
invoke active_record
create db/migrate/xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_create_moods.rb
create app/models/mood.rb
After generating model edit db/migrate/xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_create_moods.rb, add string name.
# db/migrate/xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_create_moods.rb
class CreateMoods < ActiveRecord::Migration[7.0]
def change
create_table :moods do |t|
+ t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
end
end
Next create our join table post_mood_ships, run the rails g model post_mood_ship.
root@0122:/usr/src/app# rails g model post_mood_ship
invoke active_record
create db/migrate/xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_create_post_mood_ships.rb
create app/models/post_mood_ship.rb
After generating model edit db/migrate/xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_create_moods.rb, add references for post and mood.
# db/migrate/xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_create_moods.rb
class CreatePostMoodShips < ActiveRecord::Migration[7.0]
def change
create_table :post_mood_ships do |t|
+ t.references :post
+ t.references :mood
t.timestamps
end
end
end
Open your project container and run rails db:migrate
root@a65be41abcb4:/usr/src/app# rails db:migrate
== xxxxxxxxxxxxxx CreateMoods: migrating ======================================
-- create_table(:moods)
-> 0.0509s
== xxxxxxxxxxxxxx CreateMoods: migrated (0.0510s) =============================
== xxxxxxxxxxxxxx CreatePostMoodShips: migrating ==============================
-- create_table(:post_mood_ships)
-> 0.0105s
== xxxxxxxxxxxxxx CreatePostMoodShips: migrated (0.0106s) =====================
Now, let’s move in our post , mood and post_model_ship model and set up associations.
# app/models/post.rb
class Mood < ApplicationRecord
+ has_many :post_mood_ships
+ has_many :posts, through: :post_mood_ships
end
# app/models/mood.rb
class Post < ApplicationRecord
# ...
+ has_many :post_mood_ships
+ has_many :moods, through: :post_mood_ships
# ...
end
# app/models/post_mood_ship.rb
class PostMoodShip < ApplicationRecord
+ belongs_to :post
+ belongs_to :mood
end
You can check here what is the has_many :through.
After set up association of the models. We will create default data of moods in seed under in the db/seeds.rb.
# db/seeds.rb
# ...
+ %w[Happy Angry Sad In_love].each do |name|
+ mood = Mood.create(name: name)
+ puts "create mood name: #{mood.name}"
+ end
The
%w[...]allows you to create an array without using double quotes and commas.
Then open the project container and run rails db:seed
root@a65be41abcb4:/usr/src/app# rails db:seed
Happy
Angry
Sad
In_love
Now we have default data in our mood table.
Checkbox to select multiple moods
The checkbox is commonly used to select many data, also you can able to check and uncheck.
Under the app/views/posts select _form.html.erb to edit.
<!-- app/views/posts/_form.html.erb -->
<!-- ... -->
<div>
<%= form.label :genre_id %>
<%= form.collection_radio_buttons :genre_id, Genre.all, :id, :name %>
</div>
+ <div>
+ <%= form.collection_check_boxes :mood_ids, Mood.all, :id, :name %>
+ </div>
<!-- ... -->
Under the app/controllers select posts_controller.rb to add parameter in the post.
# app/controllers/posts_controller.rb
# ...
def post_params
- params.require(:post).permit(:title, :content, :image, :address, :address_region_id, :address_province_id, :genre_id, :category_ids: [])
+ params.require(:post).permit(:title, :content, :image, :address, :address_region_id, :address_province_id, :genre_id, :category_ids: [], :mood_ids: [])
end
What is n+1 query problem?
The n+1 query problem is a problem in our database. The application creates a database query loop instead of creating one query that returns all the details. It means we call the data again and again.
To avoid N+1 Query problem, you can edit again in posts_controller in index.
# app/controllers/posts_controller.rb
#...
def index
- @posts = Post.includes(:user, :province, :region, :categories).page(params[:page]).per(5)
+ @posts = Post.includes(:user, :province, :region, :categories, :moods).page(params[:page]).per(5)
end
# ...
Before the changes, There’s many queries for moods:
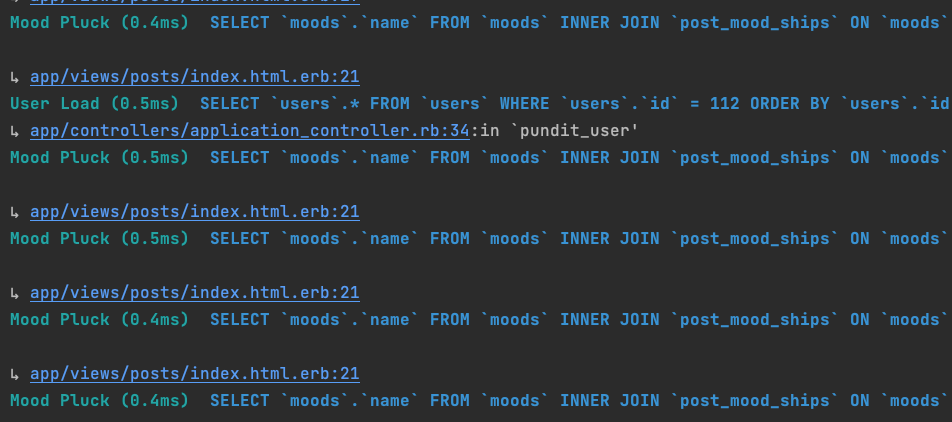
After this changes, there’s only one query for moods now:

Select2
The select2 is used when you have many options like in checkbox. If you don’t know what is select2 you can check here select2.
Let’s update the _form.html.erb under the app/views/posts.
<!-- app/views/posts/_form.html.erb -->
<!-- ... -->
<div>
<%= form.collection_check_boxes :mood_ids, Mood.all, :id, :name %>
+ <%= form.select :mood_ids, Mood.all.map { |mood| [mood.name, mood.id]}, {},
+ data: { placeholder: 'Please select moods' }, multiple: true, class: 'select2 w-25' %>
</div>
<!-- ... -->


When it comes to selecting two or more choices, the checkbox and select2 are useful. If there are fewer than five options, use checkbox. If there are lots of options (example: 100 options), use select2.