Docker Installation
Here in Kodacamp, we use Docker in creating our Ruby on Rails projects. In this part we will explore how to install a docker in your mac.

Table of contents
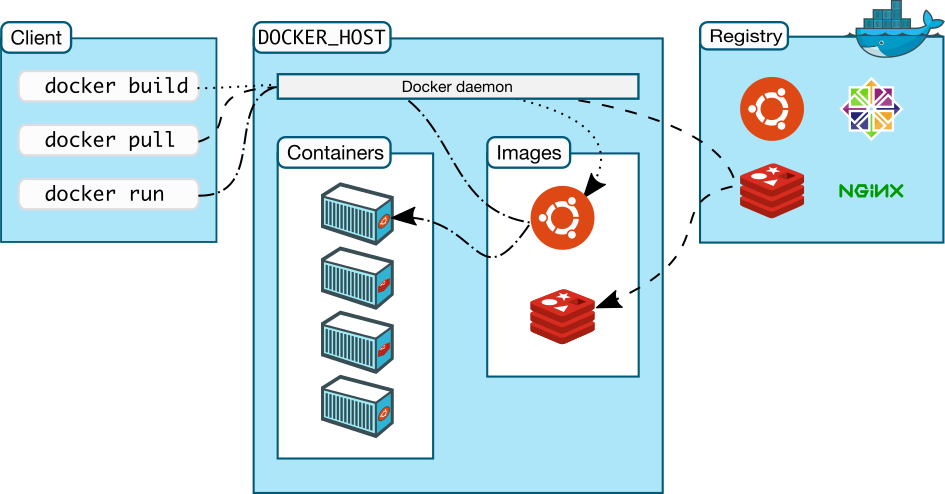
What is Docker
Before we proceed in installation, first we need to know what is docker. Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly. With Docker, you can manage your infrastructure in the same ways you manage your applications. By taking advantage of Docker’s methodologies for shipping, testing, and deploying code quickly, you can significantly reduce the delay between writing code and running it in production.
Why we use Docker
Many of the users ask the most common question: Why use docker? The answer is, Containerizing programs have a variety of advantages which include:
Portability Across Machines
You may deploy your containerized program to any other system that runs Docker after testing it. You can be confident that it will perform precisely as it did during the test.
Rapid Performance
Although virtual machines are an alternative to containers, containers do not contain an operating system (whereas virtual machines do), which implies that containers have a considerably smaller footprint and are faster to construct and start than virtual machines.
Lightweight
Containers’ portability and performance advantages can aid in making your development process more fluid and responsive. Using containers and technology like Enterprise Developer Build Tools for Windows to improve your continuous integration and continuous delivery processes makes it easier to provide the appropriate software at the right time.
Isolation
Any supporting software your application requires is likewise included in a Docker container that hosts one of your applications. It’s not a problem if other Docker containers include apps that require different versions of the same supporting software because the Docker containers are completely self-contained.
This also implies that as you progress through the stages of your development lifecycle, you can be confident that a picture you create during development will operate identically in testing and, potentially, in front of your users.
Scalability
If the demand for your apps necessitates, you can quickly generate new containers. You can use a variety of container management techniques when using multiple containers. For additional information on these choices, consult the Docker manual.
Installation
In this part we will install docker in your mac. Follow the steps and look at the images carefully.
- Download Docker from this link.
- Double-click the DMG file, and drag-and-drop Docker into your Applications folder.
You need to authorize the installation with your system password then wait for the installation to finish.
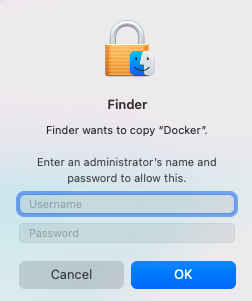
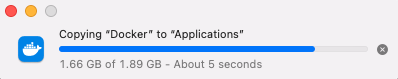
- In your
applicationsfolder orLaunchpadDouble-clickDocker.appto start Docker. - The whale in your status bar indicates Docker is running and accessible.
- Docker presents some information on completing common tasks and links to the documentation.
- You can access settings and other options from the whale in the status bar

- Open a terminal and run
docker --version $~/KodaCamp> docker --version Docker version 20.10.20, build 9fdeb9c
Docker Basic Commands
We have enlisted some docker commands to help you navigate through the docker engine.
| Command | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| docker ps | command allows us to view all the containers that are running on the Docker Host. |
| docker images | command allows us to view all the images available |
| docker stop $(docker ps -a -q); | Stop all the containers |
| docker rm $(docker ps -a -q); | Remove all the containers |
| docker rmi $(docker images -q); | Remove all the images |
| docker-compose build | Build or rebuild services |
| docker-compose up | Builds, (re)creates, starts, and attaches to containers for a service. |
| docker-compose down | Stop and remove containers, networks |