Form Radio (One-to-Many)
This page will help you how to create and use one-to-many relationships.
Table of contents
- What is One-to-Many Relationship?
- Creating Model (genre)
- Radio button
- Display genre and avoid nil errors
- Select2 (dropdown menu)
What is One-to-Many Relationship?
The one-to-many is the most common relationship. one-to-many means that there are zero or more instances of another model. It defines the relationship between the two models. For example, each post can have a genre. It displays what genre of each post.
You can check Active Record Associations for more details.
Creating Model (genre)
Let’s say our post needs genre. The relationship will be genre can have many posts and a post belongs to one genre.
We have already a post model so we only need is the genre model. Open your project container then run the rails g model genre.
root@a65be41abcb4:/usr/src/app# rails g model genre
invoke active_record
create db/migrate/xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_create_genres.rb
create app/models/genre.rb
After generating model edit db/migrate/xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_create_genre.rb, and add string name.
# db/migrate/xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_create_genres.rb
class CreateGenres < ActiveRecord::Migration[7.0]
def change
create_table :genres do |t|
+ t.string :name
t.timestamps
end
end
end
Create another migration, to add genre id to post. run rails g migration add_genre_id_to_post.
root@a65be41abcb4:/usr/src/app# rails g migration add_genre_id_to_post
invoke active_record
create db/migrate/xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_add_genre_id_to_post.rb
After migration open the file xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_add_genre_id_to_post.rb.
# db/migrate/xxxxxxxxxxxxxx_add_genre_id_to_post.rb
class AddGenreIdToPost < ActiveRecord::Migration[7.0]
def change
add_reference :posts, :genre
end
end
Open your project container and run rails db:migrate.
root@a65be41abcb4:/usr/src/app# rails db:migrate
== xxxxxxxxxxxxxx CreateGenres: migrating =====================================
-- create_table(:genres)
-> 0.0138s
== xxxxxxxxxxxxxx CreateGenres: migrated (0.0139s) ============================
== xxxxxxxxxxxxxx AddGenreIdToPost: migrating =================================
-- add_reference(:posts, :genre)
-> 0.0166s
== xxxxxxxxxxxxxx AddGenreIdToPost: migrated (0.0167s) ========================
Let’s set up associations to post and genre.
# app/models/post.rb
class Post < ApplicationRecord
+ belongs_to :genre
# ...
end
# app/models/genre.rb
class Genre < ApplicationRecord
+ has_many :posts
end
After setting up the association of the models. We will create default data of genre in seed under the db/seeds.rb.
# db/seeds.rb
# ...
+ %w[Activity Event Topic News Sport].each do |name|
+ genre = Genre.create(name: name)
+ puts "create genre name: #{genre.name}"
+ end
The
%w[...]allows you to create an array without using double quotes and commas.
Then open the project container and run rails db:seed.
root@a65be41abcb4:/usr/src/app# rails db:seed
Activity
Event
Topic
News
Sport
Now we have default data in our genre table.
Radio button
The radio button is commonly used to select one data from a set. You can also use the select2 drop-down menu.
Under the app/views/posts select _form.html.erb to edit.
<!-- app/views/posts/_form.html.erb -->
<!-- ... -->
<div>
<%= form.label :content %>
<%= form.text_field :content %>
</div>
+ <div>
+ <%= form.label :genre_id %>
+ <%= form.collection_radio_buttons :genre_id, Genre.all, :id, :name %>
+ </div>
<!-- ... -->
Under the app/controllers select posts_controller.rb to add parameter in the post.
# app/controllers/posts_controller.rb
# ...
def post_params
- params.require(:post).permit(:title, :content, :image, :address, :address_region_id, :address_province_id, :category_ids: [])
+ params.require(:post).permit(:title, :content, :image, :address, :address_region_id, :address_province_id, :genre_id, :category_ids: [])
end
The
params.require.permitallows the attributes to protect against the people trying to inject like parameters in thepostcontroller.
You can view the radio button here. http://client.com:3000/posts/new
Display genre and avoid nil errors
We need to display the genre of each post. edit the show.html.erb under the app/views/posts.
<!-- app/views/posts/show.html.erb -->
<!-- ... -->
<ul>
<!-- ... -->
+ <li><%= @post.genre.name %></li>
</ul>
<!-- ... -->
Let’s say the other posts don’t have a genre, so it will return an error called NoMethodError.
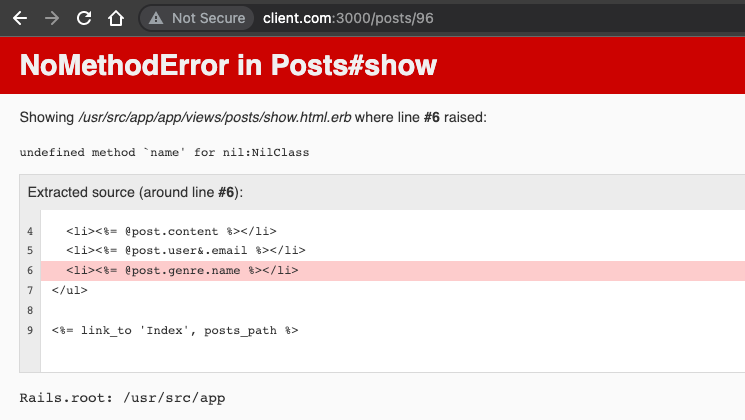
To fix that error we need to put this & before the method like this.
<!-- app/views/posts/show.html.erb -->
<!-- ... -->
<ul>
<!-- ... -->
- <li><%= @post.genre.name %></li>
+ <li><%= @post.genre&.name %></li>
</ul>
<!-- ... -->
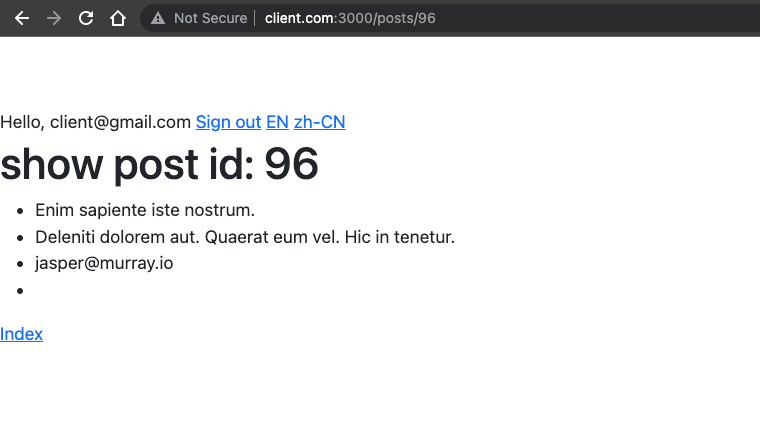
Even without genre, there’s no error will be displayed.
The
&or ampersand operator is used to call the method ongenrewithout panic that the genre may benil.
Select2 (dropdown menu)
The select2 is used when you have many options. Check select2 for guide.
Let’s update the _form.html.erb under the app/views/posts.
<!-- app/views/posts/_form.html.erb -->
<!-- ... -->
<div>
<%= form.label :genre_id %>
<%= form.collection_radio_buttons :genre_id, Genre.all, :id, :name %>
</div>
+ <div>
+ <%= form.select :genre_id, Genre.all.map { |genre| [genre.name, genre.id] }, {},
+ data: { placeholder: 'Please select genre' }, class: 'select2 w-25' %>
+ </div>
<!-- ... -->
You can view the select2 here. http://client.com:3000/posts/new
When it comes to selecting two or more choices, the radio button and select2 are useful. If there are fewer than five options, use the radio button. Use the select2 if there are lots of options (example: 100 options).